Growth factor hormone FGF21 shown to maintain a healthy metabolism
Obesity is a worldwide health problem due to its associated diseases and health disorders. The fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) hormone increases energy consumption and has beneficial effects on body weight control. It is also a novel therapeutic agent for the treatment of metabolic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. The positive effects certain diets such as vegan or the Mediterranean diet have on metabolism occur in part through FGF21.
By Diego Haro and Joana Relat Pardo
The Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a peptide hormone involved in metabolic homeostasis – or the maintenance of metabolic equilibrium. It increases energy consumption and it has beneficial effects on glucose/lipid homeostasis and on body weight control. Now it is emerging as a novel therapeutic agent for the treatment of metabolic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.
In rodent and primate models of the aforementioned conditions, FGF21 has the capacity to restore glycaemia and lipid profile, and to improve insulin resistance.
To date, therapies related to the overexpression of FGF21 undergo pharmacological administration. However, this approach has considerable limitations due to its kinetics and bioavailability.
Recently different studies have demonstrated that the endogenous levels of FGF21 and the responsiveness of tissues to FGF21 are affected by stimuli such as cold and nutritional challenges. Concretely, the FGF21 expression and signaling are regulated by fasting, high-fat diets (HFDs), ketogenic diets, some amino acid-deficient diets, low protein diets, high carbohydrate diets or specific macronutrients and bioactive dietary compounds, thus opening the possibility of inducing the production of FGF21 or increasing its activity through a dietary intervention.
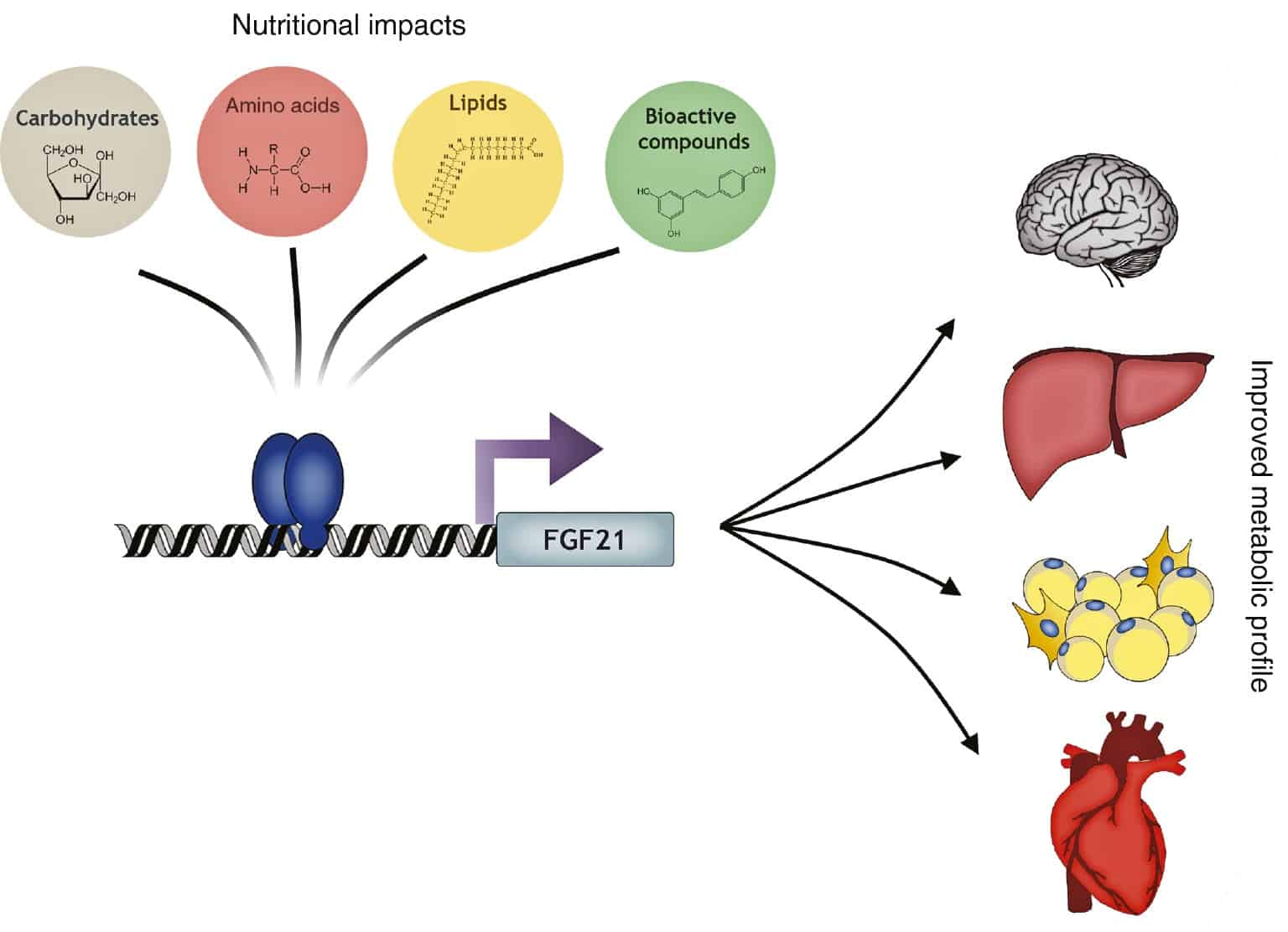
In a review published in the journal Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation, the authors compiled existing information about the mechanisms that could allow the control of endogenous FGF21 levels in order to obtain the beneficial metabolic effects of FGF21 by inducing its production instead of doing it by pharmacological administration.
The review summarizes how various nutrient stimuli and diet components regulate the expression of FGF21, and it also seeks to shed light on the molecular mechanisms and the clinical implications of the crosstalk between diet composition FGF21 levels and signaling.
Designing therapeutic approaches based on a nutritional intervention it is essential to determine the molecular mechanisms through which macronutrients, micronutrients, and bioactive dietary compounds affect metabolism and in this case FGF21 expression and signaling.
How a Mediterranean diet effects the metabolism
It is likely that the metabolic effects of certain diets such as vegan or the beneficial effects of established healthy diets, such as the Mediterranean diet, occur at least in part through FGF21. Further studies in humans will be required to define the effect of a nutritional profile on FGF21 levels and signaling in healthy, obese and type 2 diabetes patients.
Read the original article here